PCI DSS implementation
FAQ
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) is a set of security standards developed by major credit card companies to ensure the secure handling of credit card information. It applies to merchants, processors, and service providers.
Key points:
- Covers secure storage, transmission, and processing of payment card information
- Includes guidelines for security measures like firewalls, access control, and encryption
- Aims to prevent credit card fraud by protecting sensitive cardholder data
- Compliance is required for businesses accepting credit card payments
- Validated through third-party assessments by Qualified Security Assessors (QSAs)
PCI DSS applies to all organizations involved in payment card transactions:
- Merchants of all sizes
- Processors
- Acquirers
- Issuers
- Service providers
- Organizations that store, process, or transmit payment card data
- Third-party service providers handling payment card data
Compliance is mandated by major credit card brands (Visa, Mastercard, American Express, Discover, JCB). Non-compliance can result in fines, increased fees, or loss of ability to accept payment cards.
PCI DSS protects:
- Cardholder data: Primary account number, cardholder name, expiration date
- Sensitive authentication data
- The entire payment process: Point of sale/entry, transmission, storage
- Hardware, software, and networks involved in payment transactions
- The overall payment card ecosystem
Benefits:
- Prevents data breaches and security incidents
- Maintains trust in the payment card industry
- Reduces fraud risk and financial losses for consumers and businesses
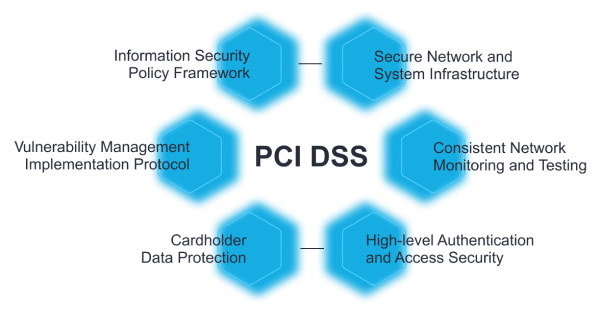
PCI DSS contains 12 requirements divided into six control objectives:
- Build and Maintain a Secure Network and Systems
- Protect Cardholder Data
- Maintain a Vulnerability Management Program
- Implement Strong Access Control Measures
- Regularly Monitor and Test Networks
- Maintain an Information Security Policy
Each requirement includes sub-requirements and implementation guidance. Compliance with all 12 requirements is mandatory for organizations handling payment card data. The standard is designed to be flexible and scalable to accommodate various organization types and processing environments.
Steps to achieve PCI DSS compliance:
- Determine applicable requirements: Identify which of the 12 requirements apply to your organization.
- Assess current security posture: Review existing controls and processes to identify gaps.
- Develop a remediation plan: Address gaps and implement necessary security controls.
- Validate compliance: Complete a Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) or undergo an on-site assessment by a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA).
- Maintain compliance: Implement ongoing monitoring and validation processes.
Note: The specific steps may vary based on organization size, complexity, and payment processing environment.
Steps for implementing a PCI DSS compliance framework:
- Scope your environment: Identify all systems involved in payment card processing.
- Conduct a risk assessment: Identify vulnerabilities, threats, and risks.
- Develop a compliance roadmap: Outline steps and timeline for achieving compliance.
- Implement security controls: Meet applicable PCI DSS requirements.
- Monitor and test: Perform ongoing security assessments.
- Validate compliance: Complete SAQ or undergo QSA assessment.
- Maintain compliance: Implement ongoing compliance management processes.
PCI DSS is important for several reasons:
- Protects cardholder data from unauthorized access or theft.
- Reduces fraud risk for consumers and businesses.
- Maintains trust in the payment card industry.
- Indirectly helps meet regulatory requirements (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
- Avoids fines and penalties for non-compliance.
Costs vary based on factors such as:
- Level of compliance required: SAQ vs. QSA assessment
- Implementation of security controls and processes
- Consulting and assessment fees
- Remediation costs
Costs can include one-time expenses and ongoing maintenance fees.
Consequences of non-compliance include:
- Fines and penalties from payment card brands
- Increased risk of data breaches
- Potential loss of ability to process payment card transactions
- Reputational damage and loss of customer trust
- Financial losses and legal liability
Overall, non-compliance can have severe and long-lasting impacts on an organization's financial health, reputation, and ability to conduct business.