Protecting corporate social resources, blogs and messengers
Every month, companies of all sizes in all countries are working to improve their services and image, trying to establish closer ties with customers, partners, and jobseekers. Social services and their integration are evolving and user expectations are rising. LinkedIn, Medium, and X (formerly Twitter) have long been the standards of corporate media. At the same time, new players are starting to take their place as corporate media: Instagram with its long captions that look like a blog, Telegram with its developed forums and crypto integrations, Discord or even TikTok, which are increasingly filled with adult professional users in addition to the younger audience.
Such developments and integrations create a huge playing field for IT companies. For example, the ability to publish tweets on X and immediately send them to Facebook saves time and expands audience reach. Another example is the ability to collect data from different platforms that suit each customer’s taste, improving service and building the company’s credibility. Finally, the automatic display of customer reviews from different social platforms on the company’s website creates the impression of transparency and instant real-time response.
However, there is another side to the coin. With the development of the Internet, scammers, fraudsters, and other criminals are also becoming more sophisticated and have more methods and tools to achieve their goals. This puts business owners at risk. The disclosure of confidential internal information affects the company’s reputation, showing its incompetence and unreliability. Leaked passwords or trade secrets to competitors can cost a company its profits or even existence. Therefore, you have to learn and apply more and more new ways to protect yourself. Let’s take a closer look at this topic.
What are the most popular incidents on social media?

You may have experienced compromising (hacking) of social media accounts or blocking them due to unfounded user complaints. These are significant problems for many users and a real disaster for some of them. What and how can businesses be affected in this regard?
Account hacking: methods used and potential losses
Using brute force attacks, data leaks, social engineering, and other methods, criminals get carte blanche to manipulate, penetrate company resources, and destroy brands. The same applies to social media resources. So let’s learn about the main ways criminals avoid danger in the future:
- Social engineering is manipulative actions that allow you to exfiltrate user data in order to take advantage of them or even threaten users in the future. This often happens when communicating via email, messengers, or anywhere else, even during a call or personal meeting.
- Phishing is a particular case of social engineering. You receive an email, a message, or even a comment on a post with a proposal for some kind of cooperation or interaction, and a link below it that will give you all the details. After you follow this link, the service requests your data, which you lose as soon as you provide it to the malicious service.
- A brute-force attack is an automated program or bot that guesses your password by numerous trials until it guesses the correct one. And they succeed in many cases sooner or later.
- Information leakage. A leak of one of your passwords puts other resources you use at risk. If some of your accounts have similar passwords or are created using personal information or the same recovery methods, it will be easier for attackers to obtain your other passwords. Anything as small as your date of birth, mother’s maiden name, pet name, or the first letter of your name can help compromise your password.
A characteristic feature of modern account hacking is the combination of the various methods described above with each other and with other attack methods, such as spam, psychological manipulation, malware, ransomware, botnets, etc.
Attacks on companies sometimes start with innocent spam. Gradually gaining unauthorized access to the company’s internal and external accounts, the attacker can expand access and eventually gain many internal accesses and data, including personal customer information, financial systems, bank accounts, or confidential projects.
It is not uncommon for files to be lost, for example, due to ransomware attacks. When many years of work are lost, it is often impossible to restore business operations.
It is also not uncommon for criminals to use company resources to mine cryptocurrencies, send spam, spread viruses, or launch further attacks on behalf of the victim. In other words, not only have you been hacked and caused damage, but you also have to prove your innocence to other crimes committed using your servers or other resources.
Thus, the business is destroyed: critical components or business processes are stopped or lost, developments and know-how are damaged, customer trust and reputation are damaged, and therefore, the company’s owners suffer huge financial losses.
Fake complaints: how it affects trust and operations

One of the most serious threats to business is fake complaints to social media administrations by malicious actors who aim to stop your business or damage your company’s reputation.
Why is it dangerous? Fake complaints can lead to a temporary blocking of your social media account, removal of content, or even complete loss of access to your account. For businesses, this means the loss of a direct channel of communication with the audience, losses, and damage to reputation. Such attacks are often organized by competitors, offended employees, partners, suppliers, or customers who seek to harm your business.
How do they do it? Attackers typically use fake accounts, bots, or hire people to file large numbers of complaints about content, claiming that it violates the platform’s rules. Due to the automated moderation systems used by most social networks, even unfounded complaints can lead to automatic restrictions on your account.
Deep counterfeiting: impact on brand image and trust
The number of deepfakes has increased. Different neural networks can easily fake audio or video. For example, the Chinese company Tencent Cloud has launched a project that allows to fake a person’s image and voice for $145 within 3 minutes. All it takes is 100 phrases spoken by a person. The service even promises the ability to make changes to the “character”: change the color of hair, eyes, skin, etc. In fact, this company’s service is a new type of Deepfakes-as-a-Service (DFaaS).
Similar stories are already happening to public figures. What if this happens, for example, to an IT company whose employees are supposed to be professionals and prevent such problems? It will be difficult to restore trust in such a company.
Spam: types, sources, and impact on user engagement

Spam is distributed mainly via email, social networks, messengers, and websites. Some examples of spam methods:
- spam accounts that may be aimed at harming particular companies;
- continuous sending of advertising emails or emails with malicious content (phishing, viruses, ransomware, etc.);
- spamming through submitting an imperfect feedback form, inappropriate or dangerous links in comments on the website, etc.
Business owners themselves suffer from spam, so they can understand how tiring it is for their employees.
On the other hand, if spammers start using the company’s resources or brand for unsolicited mailings, it will not be just individual employees who suffer, but the entire company, its domains, IP addresses, and other resources. Reputational damage can start with the loss of the ability to attract customers to promotions and end with the blacklisting of a company’s domain, up to and including the blocking of its website and email, business interruption, and criminal lawsuits for spam.
Business owners themselves suffer from spam, so they can understand how tiring it is for their employees.
On the other hand, if spammers start using the company’s resources or brand for unsolicited mailings, it will not be just individual employees who suffer, but the entire company, its domains, IP addresses, and other resources. Reputational damage can start with the loss of the ability to attract customers to promotions and end with the blacklisting of a company’s domain, up to and including the blocking of its website and email, business interruption, and criminal lawsuits for spam.
Overview of major incidents related to social media platforms
A wide audience also means serious consequences for companies. For example, in 2018, Facebook was accused of gaining access to 50 million user accounts. This compromise through the “View As” feature had serious consequences for both the company and its users.
The data breach seriously undermined users’ trust on Facebook. Many of them have become more cautious about what information they share on the platform. Facebook has faced investigations by regulators in various countries, including the US Federal Trade Commission (FTC). These investigations have resulted in significant fines. In particular, in July 2019, the FTC announced a fine of USD 5 billion.
The company faced numerous lawsuits from users who claimed that their personal data had been compromised due to flaws in Facebook’s security system. This incident was one of many that forced the global community to pay attention to the issue of personal data protection on the Internet and provoked a discussion of the need for stricter regulation of companies that process large amounts of personal information.
In 2019, the Facebook family of services was down for half a day. This halted the company’s operations and caused large-scale losses. Such incidents happened not only to Meta but also to other companies. In 2012, a Russian hacker hacked into LinkedIn and published more than a million user passwords. Here are the most popular ones:
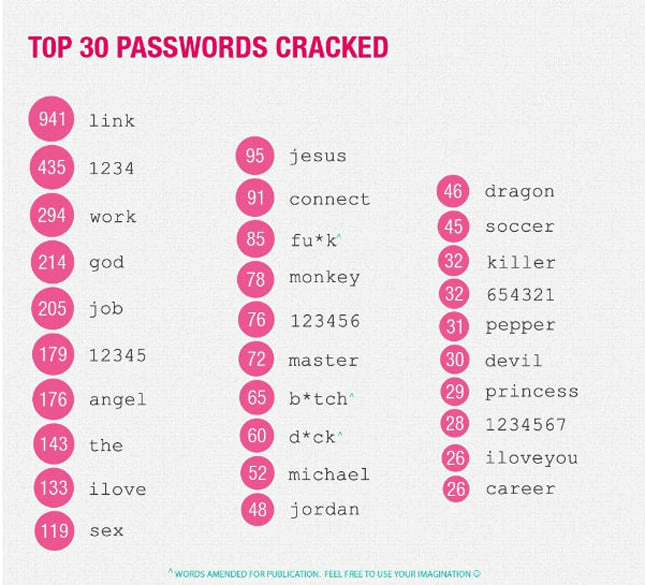
If you use such simple or even slightly more complex passwords, their fate is predetermined – sooner or later they will be stolen by hackers. So, use two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible, and elsewhere use complex passphrases instead of passwords.
Security basics for corporate social networks
Proactive security is the ability to prepare for difficult situations by acting decisively and knowing what you are doing. It is difficult for companies to prepare for unexpected attacks, such as the one by the Houthis, who damaged undersea Internet cables. However, general security measures need to be taken and events need to be monitored to stay ahead of the criminals. What are these measures?
To begin with, let’s get acquainted with the most effective general security methods and measures that are effective for social platforms and environments.
1. Develop policies for the safe use of social resources. Create and distribute clear guidelines for the safe use of social media and other social resources for work purposes to employees. The policy should specify the types of information that can be posted, security and privacy guidelines, and the measures we describe in this article. Define rules for publishing, handling comments, responding to user requests, and managing content. This will help ensure standardization and professionalism in your brand’s communications. On the other hand, create and publish clear rules of engagement for the audience of your resources to set expectations for behavior and communication. This will help to create a safe and respectful environment for communication with your audience and reduce the risk of conflicts.
2. Employee training. Hold regular cybersecurity training sessions to teach employees the basics of safe use of social media and messengers. This includes recognizing phishing messages, creating and managing strong passwords, and understanding the consequences of mishandling confidential information.
3. Multi-level authentication system. Implement a policy of mandatory 2FA for all social media and messenger accounts to have an additional layer of protection. Use apps to generate codes or SMS confirmations as a second factor after entering a password.
4. Password managers. Use strong password managers to create and store strong, unique passwords for each account. This will help avoid the risk of hacking due to reuse or insecure password storage.
5. Careful management of external links. Be cautious about posting external links in posts, messages, comments, etc., especially if they lead to resources that require a login and password. Make sure that all links are secure and do not lead to phishing sites that can be used to steal credentials. Use short links carefully, as they hide and make it difficult to monitor the final URL.
6. Review privacy and security settings. Conduct regular account security audits to ensure that your privacy and security settings are up to date with the latest requirements and best practices. Pay attention to controlling access to corporate accounts and managing user rights. This will help avoid potential violations and sanctions from platforms.

7. Security updates. Make sure that all social media applications, messengers, plugins, utilities, and other software involved are regularly updated. Monitor the release of security patches and install them immediately to protect applications from known vulnerabilities.
8. Backup. Regularly back up important information posted on social networks and messengers to prevent data loss in the event of hacking or technical failures. Develop a data recovery plan that will allow you to quickly recover lost information and minimize downtime.
9. Implement an incident response plan. Develop, maintain, and keep a plan in place to respond to other security incidents involving your social media resources besides data breaches. These may include incidents of password leakage, disclosure of trade secrets, unavailability of social media platforms, fake information, black PR, etc. The plan should include steps to minimize losses, procedures for restoring access to accounts, and support service contacts.
10. Working with the community and feedback. Pay close attention to feedback and suggestions from your community. An open dialog can help you identify potential security threats or content issues that you may not have noticed.
Finally, here’s a good quote from Myroslav Mishchenko of Fortinet about building a general protection strategy at all stages of the information and incident life cycle: “Act as if you have already been hacked. Any company must have a strategy to protect its infrastructure from external attacks and must understand what objects can be attacked (end users, critical infrastructure, etc.). The job of the Chief Security Information Officer is to correctly identify potential risks to assets and predict the actions that attackers can take with these assets. It is also important to rank the information by the level of criticality, which is the basis for building an infrastructure protection strategy. In addition, it is necessary to have a plan of action in case of a cyber incident – if the company begins to be hacked, is already being hacked, or has already been hacked.”
Platform-specific security strategies
Above, we have described the general strategies for social media security, but each network has its own specifics due to the platform’s features.

LinkedIn offers a unique set of features and capabilities for professionals and companies, which requires a specialized approach to security. In addition to general security practices, there are specific measures designed to protect LinkedIn enterprise accounts. These measures will help strengthen the protection of your account and data on this professional network.
1. Restrict the rights to publish content. Set up access rights so that only certain employees can publish content on behalf of your company. This reduces the risk of unwanted or harmful content that could damage your brand’s reputation.
2. Use the Verified Company feature. Make sure your corporate account has been verified by LinkedIn, which adds an extra layer of trust and credibility to your profile. It also reduces the likelihood of successful creation of fake accounts impersonating your brand.
3. Access management. LinkedIn offers role management, which allows you to fine-tune which employees have access to manage your corporate account. Carefully assign roles to employees according to their responsibilities, for example, administrator, editor, and analyst.
4. Regularly audit your company page. Regularly audit your company’s LinkedIn page, including checking company information, employee list, publications, and content on the page. Make sure that all data are up-to-date and do not contain information that could be used by malicious actors.
5. Pay attention to connections and messages. Be alert to connection requests and incoming messages. Train employees who have access to the corporate account to recognize the signs of phishing attacks and fraudulent messages, especially those who request confidential information.
6. Use LinkedIn’s reporting and analytics tools. Regularly analyze LinkedIn’s reports on activity on your company page to track engagement, reach, and audience response. This will help you identify any anomalies in audience behavior that may indicate a disinformation campaign or attempts to interfere with your activities on the platform.
7. Setting up filters and content moderation. Use the tools available on LinkedIn to set up filters and moderate content to prevent spam and offensive comments from being posted on your company page. This will help maintain a professional and positive image in the eyes of your audience.
Implementing these specialized security measures will help protect your LinkedIn corporate account from threats and ensure that you can use the platform safely and effectively to achieve your business goals. It’s important to review and update these measures regularly to keep up with changing security and technology conditions.
X.com

X.com (formerly Twitter) is a powerful platform for corporate communication and marketing, providing companies with the ability to quickly share news, updates, and interact with their audience. However, X’s features require special attention to the security of corporate accounts.
1. Verify your account. Strive to obtain verified status for your corporate account. A verified account with a blue checkmark not only increases the credibility of your brand but also confirms the authenticity of your account, protecting you from fakes and fake accounts.
2. Account access permissions. To manage access to your corporate account, use X Pro, X Business, and other X services that have advanced features for enterprise use, such as different levels of access for employees without having to share the password for your main X account with them.
3. Integration with official apps and services. If you use third-party apps and services to manage your X account, make sure they are reliable and reputable. Regularly check your X account security settings and revoke access to suspicious or unused apps.
4. Monitor changes to account settings. Regularly check your X corporate account settings for unexpected changes that may indicate unauthorized access. This includes changes to email, passwords, associated phone numbers, and privacy settings.
5. Protect against automated content. Use X settings and tools to combat the automated distribution of unwanted content and spam. This includes filters for comments and personal messages to help reduce the risk of harmful or spammy content impacting your brand.

Facebook offers a variety of tools and settings to protect personal and corporate information. Managing the security of corporate accounts requires a special approach. In addition to the general security guidelines described above, the following specialized measures will help strengthen the security of your business Facebook presence.
1. Set up roles for page administrators. Facebook allows you to assign different roles to users who manage a page: administrator, editor, moderator, and others. Each role has a different level of access and capabilities. Carefully choose who you assign each role to minimize the risk of unwanted actions or information leaks.
2. Use the Security Center and protect your account. Facebook provides a Security Center where you can find tips and tools to help protect your account. Set up an unusual activity alert to receive notifications when suspicious activity occurs on your page, such as logins from unusual locations or devices. This will allow you to respond quickly to potential threats.
3. Restrict access to the page through the Business Manager. Use Facebook Business Manager to manage access to your page and advertising accounts. Business Manager offers more advanced management and security tools than traditional methods. It allows you to centrally manage roles and access rights, providing a higher level of control and security.
4. Track and moderate content. Set up content moderation on your page using Facebook’s available filtering and blocking tools. This will help prevent the spread of spam, malicious links, or inappropriate comments that could threaten your company’s reputation.
5. Implement secure development principles for integrations. If your business uses Facebook integrations, such as embedded widgets on your website or automated posts through third-party apps, make sure these integrations are designed with security in mind. This includes using secure authentication methods, encrypting data, and regularly updating integrations to protect against known vulnerabilities.
6. Check applications and third-party platforms. Carefully review all third-party applications and platforms that request access to your Facebook page. Make sure they are trustworthy and have positive reviews from other users, and that you grant them only the necessary permissions.
Applying these specialized security measures to your corporate Facebook account will effectively protect your page from digital threats, ensuring that your business has a safe and productive presence on this popular social platform.
YouTube

As one of the largest video content platforms, YouTube offers many opportunities for brands and companies to promote their products and services. At the same time, effective use of YouTube requires special attention to security to protect your content, account, and reputation. Here are specialized security measures designed specifically for corporate YouTube accounts:
1. Manage access through your Google Account. Since YouTube uses Google Authentication to sign in, it’s important to carefully manage access to the Google corporate account associated with your YouTube channel. Use Google Workspace to set up and manage access so that only authorized employees have access to your YouTube account.
2. Setting up channel permissions on YouTube. YouTube allows you to assign different levels of access and roles to users on your channel, such as owner, manager, and video editor. This allows you to control who can upload videos, manage comments, and conduct analytics without giving them full access to channel management.
3. Use the channel verification feature. Verify your YouTube channel by following YouTube’s verification process. Not only does it increase the credibility of your channel among users, but it also provides additional features like uploading longer videos and customizing thumbnails.
4. Limiting information in video descriptions and metadata. Be careful with the information you post in video descriptions, metadata, and other non-obvious places. Avoid posting confidential or sensitive information that could be used against your company.
5. Comment moderation. Set up filters and moderation options for comments on your YouTube channel to prevent spam, abuse, or fraudulent links. YouTube offers tools to automatically block certain words and phrases, as well as the ability to set comments for manual approval.
6. Actively use YouTube Studio. Use YouTube Studio to manage your channel as it provides convenient tools for analytics, content moderation, and audience interaction. Regularly check your analytics for unusual changes in views or user activity that may indicate security issues.
7. Handle monetization carefully. If you use YouTube’s monetization features, make sure that your monetization settings and methods comply with YouTube’s policies and do not put your channel at risk of being blocked or otherwise sanctioned.
Implementing these specialized security measures will help keep your corporate YouTube channel safe, protect your content and audience, and reduce the risk of potential security threats. Regularly reviewing and adapting these measures in accordance with YouTube’s changing policies and the digital landscape will ensure that your channel remains secure and productive.
Telegram

Telegram is a powerful tool for corporate communication due to its features, including privacy and security. To protect corporate accounts and channels on Telegram, it is important to take specialized security measures tailored to the unique opportunities and threats associated with this messenger.
1. Verify bots. If you use Telegram bots to automate tasks or interact with customers, make sure they are verified and secure. Use only verified and trusted sources to build and manage bots to avoid data leaks or malicious activities.
2. Manage access to corporate channels and groups. Carefully control who can join your corporate channels and groups on Telegram. Use the invitation and verification features to prevent mistakes or unauthorized access to corporate communications.
3. Restrict transmission. Set up permissions in corporate groups and channels to limit who can send messages, share files, or add new members. This will help control the spread of information and avoid unwanted content.
4. Regularly check sessions of active devices. Telegram allows you to view all active sessions, i.e. the devices on which your account is currently open. Check this section in your security settings regularly and end any suspicious or unnecessary sessions.

Instagram is a key platform for brand marketing and communication due to its visual focus and wide audience. However, in order to effectively and securely use corporate Instagram accounts, specialized security measures must be taken that differ from general social media security approaches.
1. Manage access through Facebook Business Manager. For companies that use Instagram for business, it is highly recommended that you manage access to your Instagram account through Facebook Business Manager. This allows you to centrally control access, assign roles, and manage permissions without having to share Instagram logins and passwords multiple times.
2. Monitoring brand mentions. Actively use Instagram monitoring and analytics tools to track mentions of your brand. This will allow you to quickly respond to negative comments or attempts to undermine your reputation, as well as track possible unauthorized use of the brand. Regularly monitor the platform for fake accounts impersonating your brand, and contact Instagram support in a timely manner to have them removed. This will help protect your brand from negative influence and maintain audience trust.
3. Use privacy features and customize comments. Customize your business Instagram account’s privacy settings to control who can see your posts and stories. Use the comment filtering and moderation features to prevent the spread of spam, insults, or malicious links.
4. Safe use of the Instagram API. If your business integrates Instagram functionality through the API to create customized solutions, make sure that the design and development process and the resulting product comply with security best practices. All data should be transmitted over secure connections, and access to the API should be strictly controlled and limited to minimum required set of rights.
Applying these specialized security measures to corporate Instagram accounts will help ensure the protection of your information, reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches, and maintain a positive brand image on the platform.
TikTok

TikTok has become an important platform for corporate presence and marketing, engaging audiences with unique interactive content. However, to ensure the security of corporate accounts on TikTok, it is necessary to implement special security measures, taking into account the unique features and functionality of the platform.
1. Enable a private account to preview content. Use your private account to test new content formats and ideas before publishing them to your corporate account. This will help you avoid potential negative perceptions and check that the content complies with TikTok policies.
2. Restrict access to the corporate account through TikTok Pro. Use TikTok Pro features to manage your corporate account, which will provide you with additional analytics and tools for channel development. Make sure that only authorized employees have access to these features.
3. Monitoring and analyzing account activity. Regularly analyze the activity on your corporate TikTok account using built-in analytical tools. Track changes in audience, engagement, and content performance to quickly identify unusual behavior patterns that may indicate security issues.
Applying these specialized security measures will help protect your corporate TikTok account from threats and ensure safe interaction with your audience. Remember that constant attention to security issues and timely updating of security measures is the key to successful protection in the digital space.
To summarize
Now you have some insight into protecting your company’s social resources and fixing possible security errors. We’ve shown you that securing your social media accounts and data is important for building your reputation, customer satisfaction, and business growth. If you neglect security, you can irreversibly lose years of work.
If you don’t know where to start protecting your social resources or need expert assistance with complex, specific or sensitive issues, including investigations, don’t waste your time and contact us. This will reduce your costs and save time, which can be used for additional development of the company.
